本文主要介绍一下如何实现一个自己的linux文件系统,力求循序渐进。 BTW. 最好能够提前了解 linux VFS 的原理。
Overview
Linux 文件系统的核心是 VFS,VFS 是一个抽象层,可以支持各种不同的文件系统实现,例如 ext2,ext4等。这句话大多数程序员都一定是耳熟能详的了,但 VFS 究竟是怎么实现的呢?我们又应该如何去面向 VFS 来实现一个文件系统呢?
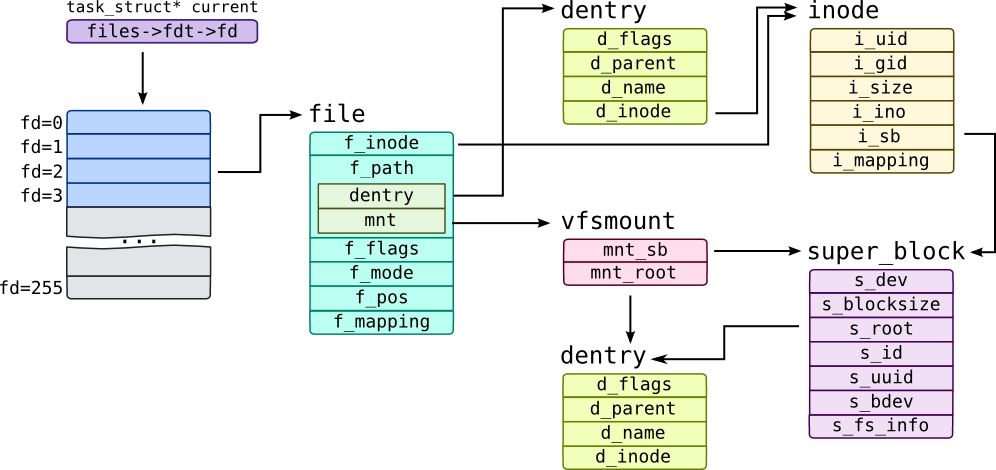
或许你已经知道,VFS 中有 Super Block,Inode,Dentry,File 等核心数据结构,但是它们之间是怎么互相联系的呢?又是怎么实现文件系统的挂载、读写等操作的呢?
Inode 对应一个具体的文件,Dentry 对应一个文件的路径,File 对应一个打开的文件,Super Block 对应一个文件系统,它们为啥要叫现在这个名字,这种命名似乎与它们的功能并不是很相关呀?我们完全可以取一套更合适的命名:File 对应一个具体的文件,Path 对应一个文件的路径,File Handle 对应一个打开的文件,FileSystem 对应一个文件系统,这样的命名似乎更加合理一些。
想要真正弄清楚这些问题还需要了解一下 VFS 的历史,这些命名方式都是从老 Unix 文件系统中继承下来的。
在 VFS 之前,Linux 系统是不支持挂载多个文件系统的,也就是说,一个系统的目录树中只有一个 ext2 文件系统。Super Block,Inode 这些数据结构都是针对 ext2 文件系统而言的,Dentry,File 也是当时为了支持 ext2 文件系统而引入的数据结构。当时的 Linux 系统中并没有 VFS 这个抽象层,所以这些数据结构都是直接定义在 ext2 文件系统的代码中的,例如 linux 0.11。后来 Linux 中开始逐步引入并完善 VFS, linux 0.99.11-patch1 这个版本中就已经出现了超级块的链表头 super_blocks,这个名字在此次变更后一直沿用到了现在。
所谓 Super Block,在 ext2 中指的是第一个 block,它包含了文件系统的基本信息,例如 block 的大小,inode 的大小,block 的数量,inode 的数量,文件系统的挂载时间,最近一次写入时间等等。在 VFS 中,Super Block 是一个对象,其中 s_fs_info 指向了具体的文件系统实现,里面的内容就是前面提到的文件系统 Super Block 中的基本信息;除此之外还有 块设备指针 s_bdev 和 s_op 函数表,里面是文件系统实现的具体操作等等等等。
而所谓 Inode,则更是 ext2 文件系统中的概念了。Inode 是 index node 的缩写,它是一个文件的索引节点,只要知道了 Inode 的编号,就可以找到对应的 Inode,从而找到文件的各个数据块。在 VFS 中,Inode 是一个表示具体目录树中具体文件结点的对象,它才不会管这个 Inode 是怎么实现的,只要通过 i_op、i_fop 函数表就可以调用到具体的文件系统实现中的操作 (所以设备也可以作为文件挂载到目录树上)。
关于这种命名定义上的变化,这篇 blog 50 years in filesystems: A detour on vnodes 有更完整的讲述。
梳理至此,我们可以这样概括一下,VFS 抽象主要提供了:
- 树形的文件组织结构,允许不同的文件系统实现都挂载到这个目录树中
- 能够根据路径,借助 dentry 来访问到相应的 inode
- 向上提供标准化的文件系统接口,向下提供标准化的文件系统实现接口
当你打开 linux 源码去查看一个具体文件系统实现的时候(例如 ext2),你会发现它们既可以被编译进内核镜像中,也可以编译成内核模块,仅在需要的时候装载进内核即可。
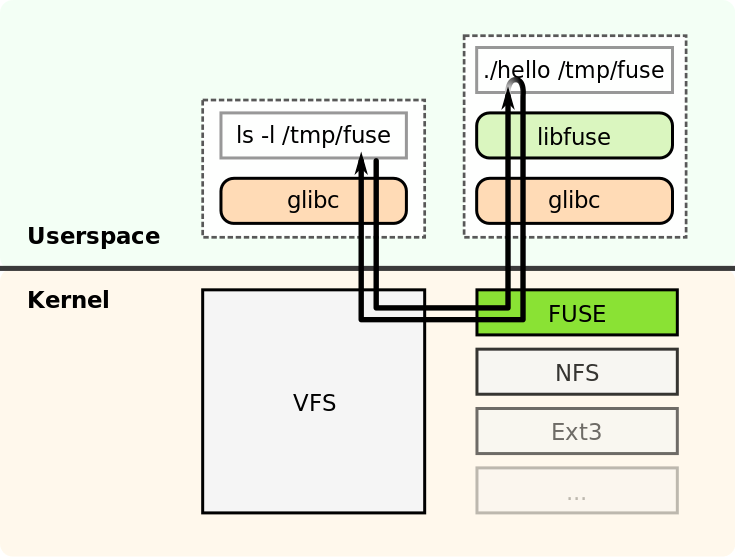
值得注意的是,用户态文件系统 fuse 与 ext2 等文件系统一样,也是一个 VFS 的实现,也是通过 register_filesystem 注册到 VFS 中,从而可以被内核 VFS 调用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
static int __init fuse_fs_init(void)
{
int err;
fuse_inode_cachep = kmem_cache_create("fuse_inode",
sizeof(struct fuse_inode), 0,
SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN|SLAB_ACCOUNT|SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT,
fuse_inode_init_once);
err = -ENOMEM;
if (!fuse_inode_cachep)
goto out;
err = register_fuseblk();
if (err)
goto out2;
err = register_filesystem(&fuse_fs_type);
if (err)
goto out3;
return 0;
out3:
unregister_fuseblk();
out2:
kmem_cache_destroy(fuse_inode_cachep);
out:
return err;
}
static int __init fuse_init(void)
{
int res;
pr_info("init (API version %i.%i)\n",
FUSE_KERNEL_VERSION, FUSE_KERNEL_MINOR_VERSION);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&fuse_conn_list);
res = fuse_fs_init();
if (res)
goto err;
res = fuse_dev_init();
if (res)
goto err_fs_cleanup;
res = fuse_sysfs_init();
if (res)
goto err_dev_cleanup;
res = fuse_ctl_init();
if (res)
goto err_sysfs_cleanup;
sanitize_global_limit(&max_user_bgreq);
sanitize_global_limit(&max_user_congthresh);
return 0;
err_sysfs_cleanup:
fuse_sysfs_cleanup();
err_dev_cleanup:
fuse_dev_cleanup();
err_fs_cleanup:
fuse_fs_cleanup();
err:
return res;
}
区别在于, fuse 并不直接与块设备交互,而是会创建一个 misc 设备,这个设备会被挂载到 /dev/fuse,用户态程序正是通过这个 misc 设备与内核进行通信,从而实现用户态文件系统的功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
static struct miscdevice fuse_miscdevice = {
.minor = FUSE_MINOR,
.name = "fuse",
.fops = &fuse_dev_operations,
};
int __init fuse_dev_init(void)
{
int err = -ENOMEM;
fuse_req_cachep = kmem_cache_create("fuse_request",
sizeof(struct fuse_req),
0, 0, NULL);
if (!fuse_req_cachep)
goto out;
err = misc_register(&fuse_miscdevice);
if (err)
goto out_cache_clean;
return 0;
out_cache_clean:
kmem_cache_destroy(fuse_req_cachep);
out:
return err;
}
所以很明显,操作系统需要能够支持 fuse.my_fs_type 这种格式的文件系统类型,并将相关操作路由到 fuse 模块,然后 fuse 的代码内部再根据 my_fs_type 来与相应的用户态进程通信。
在实际工程中,libfuse 将 fuse 的实现封装成了一个库,用户态程序只需要调用这个库提供的接口即可,而不需要关心 fuse 繁琐的细节。
由于网络上能找到的文件系统实现大多都太过复杂,很难帮人循序渐进理解文件系统,本文会先快速理一下 ext2 的源码结构,然后从零开始实现一个内核文件系统,并简单介绍一下基于 fuse 实现的 nufs,如果有时间,后续还会挖掘一下 fuse + libfuse 的实现和io数据流。
Understand a kernel filesystem: ext2
Implement file_system_type
每一个注册的文件系统都需要用一个 file_system_type 结构体来描述,其中定义了文件系统的名字以及 mount、umount 等操作的实现,例如 ext2 文件系统的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
static struct file_system_type ext2_fs_type = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "ext2",
.mount = ext2_mount,
.kill_sb = kill_block_super,
.fs_flags = FS_REQUIRES_DEV,
};
MODULE_ALIAS_FS("ext2");
然后在内核模块的初始化函数中,先初始化 inode cache,然后调用 register_filesystem 注册到 VFS 中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
static int __init init_ext2_fs(void)
{
int err;
err = init_inodecache();
if (err)
return err;
err = register_filesystem(&ext2_fs_type);
if (err)
goto out;
return 0;
out:
destroy_inodecache();
return err;
}
static void __exit exit_ext2_fs(void)
{
unregister_filesystem(&ext2_fs_type);
destroy_inodecache();
}
初始化 inode cache 即调用 slab 分配器的 kmem_cache_create() 函数来分配 ext2_inode_info 的专用高速缓存。
至此,当内核模块被装载后,操作系统就可以通过 mount -t ext2 ... 命令最终调用到 ext2_mount(), 从而挂载 ext2 文件系统了:
完整调用链路是 sys_mount - > do_mount -> do_new_mount -> vfs_get_tree -> fc->ops->get_tree(fc): legacy_get_tree -> ext2_mount -> mount_bdev(针对块设备挂载的函数,类似的还有 mount_nodev, mount_single)
ext2_mount 函数需要做的事情比较简单(调用mount_bdev):
1
2
3
4
5
static struct dentry *ext2_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data)
{
return mount_bdev(fs_type, flags, dev_name, data, ext2_fill_super);
}
在 mount_bdev 中会先搜索 ext2 文件系统的fs_supers链表,如果该设备是新挂载的设备则会调用 ext2_fill_super 函数访问磁盘上的superblock 信息,并填充 VFS super_block 对象。
super_block 中需要填充的关键内容包括:
- s_op:指向一个 super_operations 结构体,其中包含了一些回调函数,例如
alloc_inode,write_inode等,VFS 会在相应的时候调用这些回调函数。 - s_fs_info:指向具体文件系统的 super_block,这里是 ext2_sb_info 结构体。
- s_root:指向该文件系统根目录的 dentry 对象。
- s_inodes, s_dirty, s_io: 用于管理 inode 的三个链表。
- s_files: 用于管理打开的文件的链表。
super_block 对象全都以双向循环链表的形式串在一起,全局变量 super_blocks指向这个链表头部。
1
2
static LIST_HEAD(super_blocks);
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(sb_lock); /* protects super_blocks */
关于mount流程的深入分析可以参考这篇深入理解Linux文件系统之文件系统挂载 上和下
Implement super_operations
super_operations 对象提供了:
- VFS inode 对象操作相关的函数:
- alloc_inode(sb): 从上一节讲到的专用高速缓存中为 inode 对象分配内存,这里的 inode 对象是 ext2_inode_info 结构体,里面还包含 vfs_inode 对象。
- free_inode(inode) / destroy_inode(inode): 用于释放 inode 对象的内存。
- read_inode(inode):较老的linux版本中,用于从磁盘上读取 inode 信息,现在已经不再使用,现在使用 ext2_lookup->ext2_iget 填充 inode 信息。
- write_inode(inode, flag)
- dirty_inode(inode):用于更新文件系统日志,将 inode 对象标记为脏。(ext2 不支持日志功能,因此没有实现该方法)
- evict_inode(inode): vfs 的 evict 操作会将inode从各链表中移除,然后调用该方法从文件系统中删除inode,最后调用destory_inode回收内存 – called when the VFS wants to evict an inode. Caller does not evict the pagecache or inode-associated metadata buffers; the method has to use truncate_inode_pages_final() to get rid of those. Caller makes sure async writeback cannot be running for the inode while (or after) ->evict_inode() is called. Optional. From
- put_inode(inode):释放 inode(引用计数
i_count--) - drop_inode(inode):当最后一个用户unlink该inode时,在 VFS iput_final() 中,先调用该方法,然后将 inode 移出 lru 链表,最后调用 evict_inode(inode)。
- delete_inode(inode):DEPRECATED
- 文件系统操作相关的函数:
- put_super(sb):umount的时候,用于释放 super_block 对象。
- write_super(sb):DEPRECATED,用于更新 super_block。
- sync_fs(sb, wait): in place of write_super
- freeze_fs(sb)
- unfreeze_fs(sb)
- statfs(dentry, kstatfs)
- remount_fs(sb, flags, data)
- umount_begin(sb)
ext2 实现的 super_operations 如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
static const struct super_operations ext2_sops = {
.alloc_inode = ext2_alloc_inode,
.free_inode = ext2_free_in_core_inode,
.write_inode = ext2_write_inode,
.evict_inode = ext2_evict_inode,
.put_super = ext2_put_super,
.sync_fs = ext2_sync_fs,
.freeze_fs = ext2_freeze,
.unfreeze_fs = ext2_unfreeze,
.statfs = ext2_statfs,
.remount_fs = ext2_remount,
.show_options = ext2_show_options,
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
.quota_read = ext2_quota_read,
.quota_write = ext2_quota_write,
.get_dquots = ext2_get_dquots,
#endif
};
Implement file_operations & inode_operations for directory
这里 inode_operations 是处理文件系统中 inode 读写的,而 file_operations 是处理文件内容读写相关的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
const struct file_operations ext2_dir_operations = {
.llseek = generic_file_llseek,
.read = generic_read_dir,
.iterate_shared = ext2_readdir,
.unlocked_ioctl = ext2_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = ext2_compat_ioctl,
#endif
.fsync = ext2_fsync,
};
// dir
const struct inode_operations ext2_dir_inode_operations = {
.create = ext2_create,
.lookup = ext2_lookup,
.link = ext2_link,
.unlink = ext2_unlink,
.symlink = ext2_symlink,
.mkdir = ext2_mkdir,
.rmdir = ext2_rmdir,
.mknod = ext2_mknod,
.rename = ext2_rename,
.listxattr = ext2_listxattr,
.getattr = ext2_getattr,
.setattr = ext2_setattr,
.get_acl = ext2_get_acl,
.set_acl = ext2_set_acl,
.tmpfile = ext2_tmpfile,
.fileattr_get = ext2_fileattr_get,
.fileattr_set = ext2_fileattr_set,
};
// symlink
const struct inode_operations ext2_symlink_inode_operations = {
.get_link = page_get_link,
.getattr = ext2_getattr,
.setattr = ext2_setattr,
.listxattr = ext2_listxattr,
};
const struct inode_operations ext2_fast_symlink_inode_operations = {
.get_link = simple_get_link,
.getattr = ext2_getattr,
.setattr = ext2_setattr,
.listxattr = ext2_listxattr,
};
Implement file_operations & inode_operations for file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
const struct file_operations ext2_file_operations = {
.llseek = generic_file_llseek,
.read_iter = ext2_file_read_iter,
.write_iter = ext2_file_write_iter,
.unlocked_ioctl = ext2_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = ext2_compat_ioctl,
#endif
.mmap = ext2_file_mmap,
.open = dquot_file_open,
.release = ext2_release_file,
.fsync = ext2_fsync,
.get_unmapped_area = thp_get_unmapped_area,
.splice_read = generic_file_splice_read,
.splice_write = iter_file_splice_write,
};
const struct inode_operations ext2_file_inode_operations = {
.listxattr = ext2_listxattr,
.getattr = ext2_getattr,
.setattr = ext2_setattr,
.get_acl = ext2_get_acl,
.set_acl = ext2_set_acl,
.fiemap = ext2_fiemap,
.fileattr_get = ext2_fileattr_get,
.fileattr_set = ext2_fileattr_set,
};
Implement address_space_operations for cacheable, mappable objects
主要 fields 是writepage,write_begin 和 write_end 等函数指针,功能都是维护 page cache 与文件之间的映射关系。
Build a kernel filesystem: toyfs
toyfs 当前是一个及其简短的文件系统,为了降低复杂性,当前版本所有的内容都保存在内存中,避免了块设备的操作,对内核初学者来说更易上手。
Build a fuse filesystem: nufs
前面讲到过,FUSE 也是一个对接 VFS 的内核模块的具体实现,但 FUSE 并不会直接与任何存储介质交互,而是通过一个 misc 设备与用户态的 fuse daemon 通信从而实现文件系统的功能。